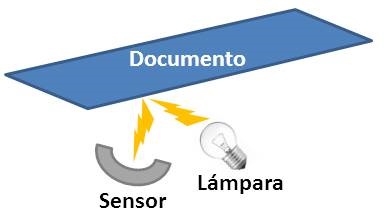
How a scanner works?
In this post we are going to offer you a lot of information about scanners. After reading this post you will be an expert in scanners.
1. Kinds of scanners
There are several kinds of scanner in the market depending on the use. However, the most common are the scanners of document that are designed to scan documents or images. In the next picture you have the most used scanners of documents:
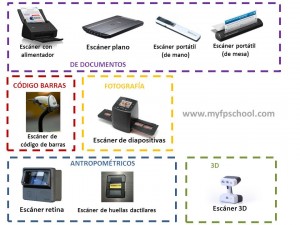
kinds of scanners
The portable models are used when you travel with them. Remember that the quality of those scanners is worst than a bigger one because they have less resolution.
Barcode scanners. The barcode scanners are used mainly in shops, stores, etc. The barcode is an effective system to recognize the code of a product. There are several kinds of barcode scanners like the fixed scanners, the pistol scanners, etc.
Scanners of negatives. They were very popular years ago because a lot of people wanted to change their analog photos to digital photos. There were professional scanners and home scanners. The difference between them were the quality and also the price.
Anthropometric scanners. This kind of scanner uses anthropometric data of the people in order to determine their identity. However, the most used are the finger print scanners that uses the patterns in your finger print to identify you. Another kind of anthropometric scanners are the iris scanner and retinal scanner, both are very effective.
3D scanners. The 3D scanners are very popular because of the 3D printers demand. These scanners take several points around the surface of an object. With this points and the use of a technique called extrapolation, the printer can clone the object. Sometimes in order to get a more realistic object, the scanner also takes samples of the color.
2. The parameters of a scanner.
Size of the document to scan. Is one of the main parameters to take into account. The most used is the A4 or the letter size. The size of an A4 is 216 x 297 milimiters.
Previsualization time. Is the time that the scanner takes to scan the document and show to the user. A normal time use to be 9 seconds approximately.
Resolution and interpolation. The resolution depends on the model of the scanner. Some scanner have more quality meanwhile others have a bigger scanning surface. The resolution is expresed in points per inch (ppp) or dots per inch (dpi).
The optical resolution is different that the hardware resolution. For example, an scanner can have a 4800 dpi optical resolution but a maximum 12800 dpi resolution. That means that there are 4800 sensors in a row scanning the document with a final 4800 x 9600 dpi hardware resolution. The hardware deduces extra pixels in between the real ones in order to get a better resolution.
Light. The source of light has been changing along the years. Firstly, fluorescent lights were used. Nowadays the cold cathodes are been replaced by LED lights because they are cheaper and have the same lumens.
Scanning buttons. Most of the systems nowadays have others functions than scanning like make a photocopy, generate a PDF, send the document by email, etc.
Maximum scan area. Generally expressed in inches. Is the maximum area that the scanner can work with. For example, 8.5″ x 11.7″.
Color depth. Is the number of bits used to display the color of a pixel. For example, 48 bits.
Resumen
Nombre del artículo
How a scanner works?
Descripción
In this post we are going to offer you a lot of information about scanners. After reading this post you will be an expert in scanners.
Autor
Juan Carlos Moreno